Consequences of Hypernatremia
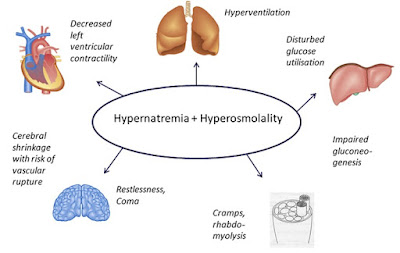
Hypernatremia and the resulting hyperosmolar state impact various bodily functions. One well-known consequence is its influence on neurological function. The occurrence of hypernatremia and subsequent hyperosmolality triggers a movement of free water from within cells to the extracellular space. This shift results in the shrinkage of brain cells, potentially leading to vascular rupture and persistent neurological impairments in severe cases. Cerebral demyelination, a feared complication in addressing hyponatremia, has also been observed in hypernatremia cases of diverse origins. Individuals with end-stage liver disease who develop hypernatremia appear particularly susceptible to cerebral demyelination.